For a while now I wanted to try out EVPN on the MX. I decided to go for the easiest of scenarios that EVPN has to offer: a single-homed VLAN-based EVPN:
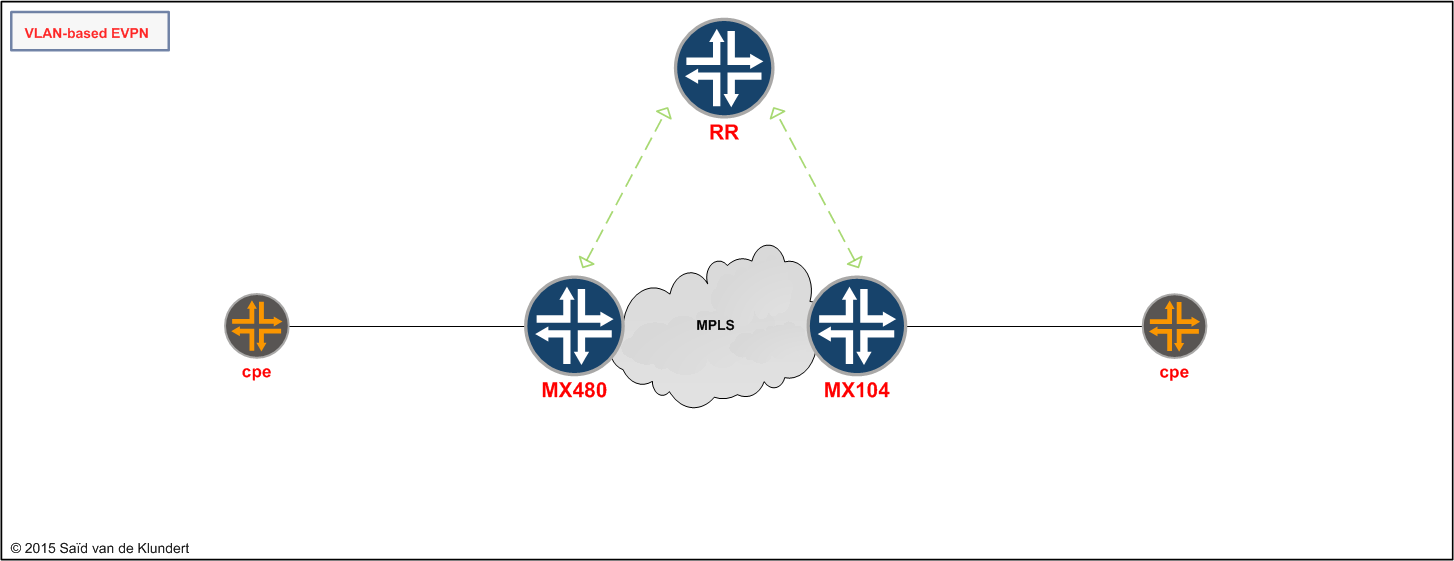
There is a lot to tell about EVPN. For instance, EVPN uses MP-BGP in a way that is similar to MPLS VPN and MAC learning does not occur in the data plane but in the control plane. While there is a lot of interesting theory to go on about, the focus in this article is to keep it simple and short. First, I'll ready the MX for EVPN. After that, I’ll go through the configuration and verification.
Readying the MX for EVPN
The MX has to run in ’enhanced-ip mode’ and the forwarding table needs to be able to handle and configure chained composite next-hops. These things are configured using the following commands:
set chassis network-services enhanced-ip set routing-options forwarding-table chained-composite-next-hop ingress evpn
Changing the network-services requires a reboot.
Configuring a single-homed VLAN-based EVPN
On the MX480, the configuration relevant for the EVPN is as follows (complete configuration found via link at the end):
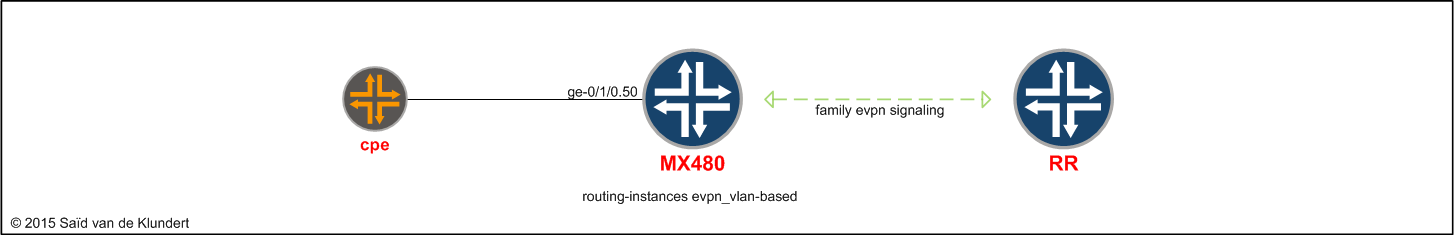
set interfaces ge-0/1/0 flexible-vlan-tagging set interfaces ge-0/1/0 encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 50 description CPE_EVPN set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 50 encapsulation vlan-bridge set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 50 vlan-id 50 set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 50 family bridge set protocols bgp group rr family evpn signaling set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based instance-type evpn set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based vlan-id 50 set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based interface ge-0/1/0.50 set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based route-distinguisher 3:3 set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based vrf-target target:3:3 set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based protocols evpn
Verifying a single-homed VLAN-based EVPN
After finishing the configuration on the different nodes, let’s start by having a look at the network diagram again;
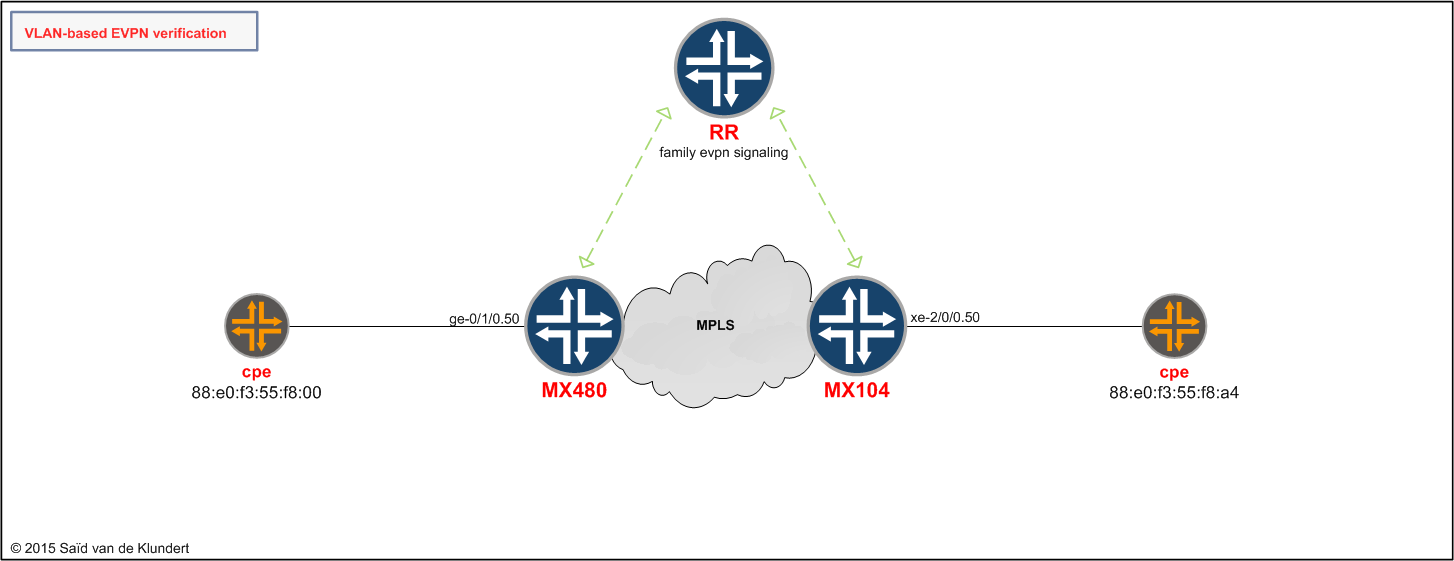
After generating some traffic between the CPE’s, we can observe the following on the MX480:
play@MX480-TEST-RE0> show bgp summary
Groups: 1 Peers: 1 Down peers: 0
Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending
bgp.evpn.0
2 2 0 0 0 0
Peer AS InPkt OutPkt OutQ Flaps Last Up/Dwn State|#Active/Received/Accepted/Damped...
1.1.1.1 1 11 10 0 0 2:32 Establ
bgp.evpn.0: 2/2/2/0
__default_evpn__.evpn.0: 0/0/0/0
evpn_vlan-based.evpn.0: 2/2/2/0
The BGP session with the route-reflector is established and routes are exchanged. The EVPN routes are stored in the ‘bgp.evpn.0’ table . Here we can see the individual mac-addresses learned from the remote PE as well (only one in our case):
play@MX480-TEST-RE0> show route receive-protocol bgp 1.1.1.1 table bgp.evpn.0 bgp.evpn.0: 2 destinations, 2 routes (2 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) Prefix Nexthop MED Lclpref AS path 2:3:3::50::88:e0:f3:55:f8:a4/304 * 1.1.1.20 100 I 3:3:3::50::1.1.1.20/304 * 1.1.1.20 100 I
To see what MAC addresses are learned in the EVPN (and where), you can issue the following commands:
play@MX480-TEST-RE0> show evpn mac-table
MAC flags (S -static MAC, D -dynamic MAC, L -locally learned, C -Control MAC
O -OVSDB MAC, SE -Statistics enabled, NM -Non configured MAC, R -Remote PE MAC)
Routing instance : evpn_vlan-based
Bridging domain : __evpn_vlan-based__, VLAN : 50
MAC MAC Logical NH RTR
address flags interface Index ID
88:e0:f3:55:f8:00 D ge-0/1/0.50
88:e0:f3:55:f8:a4 DC 1048589 1048589
play@MX480-TEST-RE0> show evpn database
Instance: evpn_vlan-based
VLAN MAC address Active source Timestamp IP address
50 88:e0:f3:55:f8:00 ge-0/1/0.50 Jul 25 18:24:15
50 88:e0:f3:55:f8:a4 1.1.1.20 Jul 25 17:52:05
These self-explanatory commands offer a lot of options. For instance, it’s possible to narrow down to remotely learned MAC addresses in a specific instance. You will even be able to see what time the MAC address was learned:
play@MX480-TEST-RE0> show evpn database origin remote vlan-id 50 instance evpn_vlan-based Instance: evpn_vlan-based VLAN MAC address Active source Timestamp IP address 50 88:e0:f3:55:f8:a4 1.1.1.20 Jul 25 17:52:05
Not really necessary in a lab with 2 PE routers, 1 instance and 1 VLAN, but very nice nevertheless!
Before firing up your own EVPN lab, bear in mind that you cannot configure ‘instance-type evpn’ in a logical system. At least not on an MX480 running 14.2R3.8, which was what I was running. In this and newer versions of Junos, you can also skip the configuration of the forwarding-table under routing-options. It is already inherited from ‘junos-defaults’:
play@MX480-TEST-RE0> show configuration routing-options forwarding-table | display inheritance defaults
##
## 'chained-composite-next-hop' was inherited from group 'junos-defaults'
##
chained-composite-next-hop {
##
## 'ingress' was inherited from group 'junos-defaults'
##
ingress {
##
## 'evpn' was inherited from group 'junos-defaults'
##
evpn;
}
}
There is a lot more to tell and learn about EVPN and I’ll try to post any new insights I gain. Until I have, I can recommend ‘Using Ethernet VPNs for Datacenter Interconnect’ by Victor Ganjian. A day one book you can download for free from the Juniper website. You can also check out the RFC itself. Lastly, the configuration used for the MX104 and MX480 is the following:
MX480:
set chassis network-services enhanced-ip set interfaces ge-0/1/0 flexible-vlan-tagging set interfaces ge-0/1/0 encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 50 description CPE_EVPN set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 50 encapsulation vlan-bridge set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 50 vlan-id 50 set interfaces ge-0/1/0 unit 50 family bridge set routing-options autonomous-system 1 set protocols bgp local-address 1.1.1.21 set protocols bgp out-delay 2 set protocols bgp log-updown set protocols bgp group rr type internal set protocols bgp group rr family evpn signaling set protocols bgp group rr authentication-key "$9$CVAyuOIyrKvWXVwGjHmQz" set protocols bgp group rr peer-as 1 set protocols bgp group rr neighbor 1.1.1.1 description Aurelius_rr set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based instance-type evpn set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based vlan-id 50 set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based interface ge-0/1/0.50 set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based route-distinguisher 3:3 set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based vrf-target target:3:3 set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based protocols evpn
MX104:
set chassis network-services enhanced-ip set interfaces xe-2/0/0 flexible-vlan-tagging set interfaces xe-2/0/0 encapsulation flexible-ethernet-services set interfaces xe-2/0/0 unit 50 description CPE_EVPN set interfaces xe-2/0/0 unit 50 encapsulation vlan-bridge set interfaces xe-2/0/0 unit 50 vlan-id 50 set interfaces xe-2/0/0 unit 50 family bridge set routing-options autonomous-system 1 set routing-options forwarding-table chained-composite-next-hop ingress evpn set protocols bgp local-address 1.1.1.20 set protocols bgp out-delay 2 set protocols bgp log-updown set protocols bgp group rr type internal set protocols bgp group rr family evpn signaling set protocols bgp group rr authentication-key "$9$CVAyuOIyrKvWXVwGjHmQz" set protocols bgp group rr peer-as 1 set protocols bgp group rr neighbor 1.1.1.1 description Aurelius_rr set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based instance-type evpn set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based vlan-id 50 set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based interface xe-2/0/0.50 set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based route-distinguisher 3:3 set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based vrf-target target:3:3 set routing-instances evpn_vlan-based protocols evpn